The water hardness
Water described as “hard” has a high concentration of dissolved minerals, specifically calcium and magnesium ions. Hard water does not present a health risk nor does it have a negative effect on the environment although it is a nuisance and causes added expenses.
Temporary hardness is caused by carbonates and can be eliminated by boiling or by adding lime -Ca(OH)2 (Calcium Hydroxide)- to the water. Calcium carbonate is less soluble in hot water than in cold so that when the water is boiled the bicarbonate is precipitated out of the solution leaving the water softer.
Permanent water hardness cannot be eliminated by boiling and is due to the presence of calcium and magnesium or chlorides, which are more soluble at higher temperatures. Despite its name this sort of hardness can be eliminated using sodium sulfate.
(Very soft water / Soft water / Hard water / Very hard water / Extremely hard water)
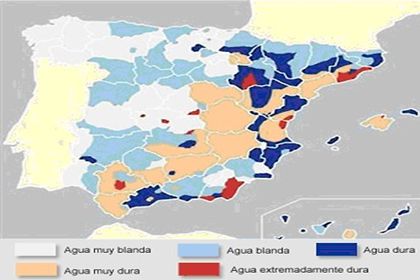
Map showing hard water zones in Spain
The drinking water supplied by the Municipal Water Service comes from the inland area of the Marina Alta, characterized by limestone mountains through which the rain water runs and filters to the aquifers resulting in concentrations of dissolved calcium of approximately 200 mg/l and therefore can be classified as HARD WATER.
The effects of hard water are:
- The use of more detergents for clothes washing. In laundering clothes larger quantities of detergents or soap have to be used in order to get good results. Hard water interferes with soap and detergent performance because the positively charged ions partially inactivate the principal active ingredients.
- More soap and shampoo for personal hygiene with poorer results because the same occurs as with detergent. It is more difficult to work up a lather resulting in dry skin and dull lank hair.
- More salt needed in the dishwasher to keep the appliance’s water softening systems clean permitting better results. If salt is not used dishes and glasses may be spotted and dull when dry. Lime-scale deposits can form on the water heating elements of the appliance contributing to inefficient operation or failure.
- Danger of blocked pipes. The accumulation of lime-scale, especially in hot water pipes and water heaters, can clog up pipes and reduce the life of water heaters.
Classification of the hardness |
|||||
| Mg/l de CaCo3 | º French | DegreesClark ºe | Deutsche Härte ºdH |
Water type |
|
| 0 - 3 | 3º | 1,19º | 0,95º | soft | |
| abr-60 | 3º - 6º | 1,19º - 4,20º | 0,95º - 3,35 |
moderately soft |
|
| 61 - 120 | 6º - 12º | 3,35º - 8,39º |
slightly hard |
||
| 121 - 180 | 12º - 18º | 8,39º - º10,05º |
moderately hard |
||
| 181 - 250 | 18º - 25º | 4,20º - 12,59º | 10,05º - 12,41º | hard | |
| . + 250 | .+ 25º | .+ 12,59º | .+ 12,41º |
Very hard |
|
Ways to prevent the negative effects of hard water:
- Laundry: According to the manufacturers, powder gives better results than liquid detergents in hard water. To obtain optimum results it must be taken into account that detergents are formulated for moderately hard water and therefore give dosage instructions according to the different sorts of water and degree of dirt. It is recommended to use higher doses in hard water areas and follow the manufacturers washing instructions. Unlike dishwashers, washing machines don’t have water-softening systems since 75% of the washing cycles used employ cold water and therefore no lime scale is produced. Water softeners can be used to neutralize the water’s hardness in hot washes.
When hard water is used for washing, lime scale can’t actually be seen on the clothes although these do become rough due to a build up of incrusted lime.
- Washing crockery & cutlery in a dishwasher: The first thing we should do is to adjust the setting of the appliance to the hardness of the water used. Dishwashers heat up the water used to over 35 to 40 degrees Celsius, temperature at which precipitation occurs and lime-scale is formed. In order to prevent this, these appliances use synthetic resin filters that trap the particles and soften the hard water. These filters must be washed regularly in order to maintain their efficiency. This is why salt is used.



Domestic appliances effected by hard water
- Skin and hair: Skin can be re-hydrated or lubricated if it becomes dry. For example after showering oil can be rubbed onto wet skin to get results 15 to 20 seconds. Another method is to apply body lotion although this is more expensive and time-consuming process. Hair is as delicate as the skin and can also effected by exogenous agents and should also be given special care in the form of shampoos with oily additives.
- Watering plants: Add a few drops of vinegar or lemon juice to the water,
- Cleaning taps: Wrap taps with toilet paper or bandages and soak these with vinegar. Leave overnight and then rinse with plenty of water.
- Cleaning the bathroom: Rub lime-scale with a cloth soaked in hot white vinegar. Rinse with plenty of water. The operation should be repeated until the stains have disappeared. If yellow stains appear these can be removed by rubbing with bleach.
- De-scaling iron soleplates: Fill the iron with vinegar and turn on until this evaporates. Then clean the vents in the soleplate with a cotton bud soaked in Vinegar.


 Castellano
Castellano  Valencià
Valencià  Deutsch
Deutsch  English (UK)
English (UK) 